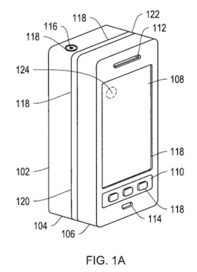
With a fresh patent in hand this week for facial recognition, a fingerprint reader on its iPhone 5 and a new $345 million acquisition of 3D-sensor company PrimeSense , Apple seems to be putting some serious body english on the user interface. Apple’s Facial Recognition patent image points to an "image sensor" behind the screen. Is Apple gunning to re-define interacting (re: authentication) and interfacing with computers, devices -and ultimately "things" in the computing environment at large?
And will it re-set expectations for security, as well as, for innovation and convenience? Apple’s newest patent awarded by the U.S. Patent and Trademark office points to a sophisticated array of biometric and gesture-based inputs across a range of devices and vertical industries. If that is the case (the company isn’t saying), can Apple’s pedigree for elegant design overcome fickle user acceptance and current shortcomings in biometric technology and lap the field?
"The state of play today in consumer biometrics security is pretty primitive," said Steve Wilson, vice president and principal analyst at Constellation Research. "In security, we’re accustomed to rigorous standards and testing; lots of peer review; all encryption algorithms being published. But with biometrics we still don’t have agreed upon test protocols." Wilson said consumer biometrics is all about convenience and has very little to do with serious security.
Apple found that out first hand when the Touch ID fingerprint reader on the new iPhone 5 was hacked shortly after introduction[…]
Source www.zdnet.com
Source: zdnet.com
